AtCoder Beginner Contest 120 题解
分类:
IT文章
•
2023-11-13 08:56:01
题目链接:https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc120
A Favorite Sound
分析:答案为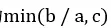 。
。
代码:
![]()
1 #include <iostream>
2
3 using namespace std;
4
5 int main()
6 {
7 int a, b, c;
8 cin>>a>>b>>c;
9 cout<<min(b / a, c)<<endl;
10 return 0;
11 }
View Code
B K-th Common Divisor
分析:A、B范围很小,枚举即可。注意要判断A、B的大小,从大到小枚举。
代码:
![]()
1 #include <cstdio>
2 #include <iostream>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int a, b, k;
9 scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &k);
10 int imax = max(a, b);
11 int cnt = 0;
12 for(int i = imax; i >= 1; --i)
13 {
14 if(a % i == 0 && b % i == 0)
15 cnt++;
16 if(cnt == k)
17 {
18 printf("%d
", i);
19 break;
20 }
21 }
22 return 0;
23 }
View Code
C Unification
分析:因为S串里只有‘0’和‘1’,所以无论如何只要还有‘0’和‘1’同时存在,就一定可以继续该操作。答案就是‘0’和‘1’的数量取最小值的两倍(一次操作两个cube)。
代码:
![]()
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <cstdio>
3 #include <cstring>
4
5 using namespace std;
6
7 int main()
8 {
9 char s[100005];
10 scanf("%s", s);
11 int slen = strlen(s);
12 int zero = 0, one = 0;
13 for(int i = 0; i < slen; ++i)
14 {
15 if(s[i] == '0')
16 zero++;
17 else if(s[i] == '1')
18 one++;
19 }
20 printf("%d
", min(zero, one)*2);
21 return 0;
22 }
View Code
![]()
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <cstdio>
3
4 using namespace std;
5
6 typedef long long ll;
7
8 struct bridge
9 {
10 int a;
11 int b;
12 }dict[100005];
13
14 int parent[100005], trank[100005];
15 ll sum;
16 ll ans[100005] = {0};
17 ll s[100005];
18
19 void init()
20 {
21 for(int i = 0; i < 100005; ++i)
22 {
23 parent[i] = -1;
24 trank[i] = 0;
25 }
26 }
27
28 int find_root(int x)
29 {
30 int x_root = x;
31 while(parent[x_root] != -1)
32 x_root = parent[x_root];
33 return x_root;
34 }
35
36 int union_set(int x, int y)
37 {
38 int x_root = find_root(x);
39 int y_root = find_root(y);
40 if(x_root == y_root)
41 return 0;
42 else
43 {
44 if(trank[x_root] > trank[y_root])
45 {
46 parent[y_root] = x_root;
47 sum -= s[x_root]*s[y_root];
48 s[x_root] += s[y_root];
49 }
50 else if(trank[y_root] > trank[x_root])
51 {
52 parent[x_root] = y_root;
53 sum -= s[x_root]*s[y_root];
54 s[y_root] += s[x_root];
55 }
56 else
57 {
58 parent[y_root] = x_root;
59 trank[x_root]++;
60 sum -= s[x_root]*s[y_root];
61 s[x_root] += s[y_root];
62 }
63 }
64 return 1;
65 }
66
67 int main()
68 {
69 init();
70 int n, m;
71 scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
72 for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
73 scanf("%d %d", &dict[i].a, &dict[i].b);
74 for(int i = 0; i <= n; ++i)
75 s[i] = 1;
76 sum = 1ll*n*(n-1)/2;
77 for(int i = m - 1; i >= 0; --i)
78 {
79 ans[i] = sum;
80 int x = dict[i].a;
81 int y = dict[i].b;
82 union_set(x, y);
83 }
84 for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
85 cout<<ans[i]<<endl;
86 return 0;
87 }
。
