二叉树的N中搜索方式和拓展应用
分类:
IT文章
•
2022-04-22 08:49:10
(一)创建二叉树,如下图所示,一个标准的二叉树是所有位于根节点的左侧的子节点都是比根节点小的,右侧则都是大于根节点的。

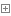
public class BinaryNode
{
public int val;
public BinaryNode left;
public BinaryNode right;
public BinaryNode(int val)
{
this.val = val;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
public static BinaryNode createBinaryTree(int[] array)
{
BinaryNode root = new BinaryNode(array[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < array.Length; i++)
{
insertBinaryTreeNode(root, array[i]);
}
return root;
}
private static void insertBinaryTreeNode(BinaryNode root, int val)
{
if(root.val >= val)
{
if (root.left == null)
{
root.left = new BinaryNode(val);
return;
}
else
{
insertBinaryTreeNode(root.left, val);
}
}
else
{
if (root.right == null)
{
root.right = new BinaryNode(val);
return;
}
else
insertBinaryTreeNode(root.right, val);
}
}
}
createBinaryTree
(二)前序遍历:根节点-左节点-右节点(即输出为:8,3,2,1,5,4,6,20,15,13,16,29,21,30)

public static List<int>preOrderTraverse(BinaryNode root)
{
List<int> nodes = new List<int>();
subPreOrderTraverse(root, nodes);
return nodes;
}
private static void subPreOrderTraverse(BinaryNode root, List<int> nodes)
{
if(root != null)
{
nodes.Add(root.val);
subPreOrderTraverse(root.left, nodes);
subPreOrderTraverse(root.right, nodes);
}
}
preOrderTraverse
不使用递归方法实现的前序遍历,即深度优先遍历(depth first search, DFS),使用栈实现。

public static List<int>depthFirstSearch(BinaryNode root)
{
Stack<BinaryNode> stack = new Stack<BinaryNode>();
stack.Push(root);
List<int> nodes = new List<int>();
while (stack.Count != 0)
{
BinaryNode node = stack.Pop();
nodes.Add(node.val);
if (node.right != null)
stack.Push(node.right);
if (node.left != null)
stack.Push(node.left);
}
return nodes;
}
depthFirstSearch
(三)中序遍历:左节点-根节点-右节点(即输出为:1,2,3,4,5,6,13,15,16,20,21,29,30)。可见中序遍历的特点是输出的是升序数组。

public static List<int>inOrderTraverse(BinaryNode root)
{
List<int> nodes = new List<int>();
subInOrderTraverse(root, nodes);
return nodes;
}
private static void subInOrderTraverse(BinaryNode root, List<int> nodes)
{
if (root != null)
{
subInOrderTraverse(root.left, nodes);
nodes.Add(root.val);
subInOrderTraverse(root.right, nodes);
}
}
inOrderTraverse
中序遍历的非递归方法实现,同样使用栈。

public static List<int>inOrderTraverseNonRecursion(BinaryNode root)
{
List<int> nodes = new List<int>();
Stack<BinaryNode> stack = new Stack<BinaryNode>();
BinaryNode node = root;
while(node!=null || stack.Count != 0)
{
if (node != null)
{
stack.Push(node);
node = node.left;
}
else
{
node = stack.Pop();
nodes.Add(node.val);
node = node.right;
}
}
return nodes;
}
inOrderTraverseNonRecursion
根据中序遍历能得到升序的数组的特点,可以用于解决验证二叉树的问题。leetcode98:给定一个二叉树,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。解题思路便可以使用中序遍历得到数组,判断是否为升序数组。

public static bool IsValidBST(BinaryNode root)
{
List<int> nodes = new List<int>();
subIsValidBST(root, nodes);
if (nodes.Count > 1)
return false;
else
return true;
}
private static void subIsValidBST(BinaryNode root,List<int>nodes)
{
if (root != null)
{
subIsValidBST(root.left, nodes);
nodes.Add(root.val);
if (nodes.Count > 1)
{
if (nodes[1] <= nodes[0])
return;
else
nodes.RemoveAt(0);
}
subIsValidBST(root.right, nodes);
}
}
isValidBST
(四)后序遍历:左节点-右节点-根节点(即输出为:1,2,4,6,5,3,13,16,15,21,30,29,20,8)

public static List<int>postOrderTraverse(BinaryNode root)
{
List<int> nodes = new List<int>();
subPostOrderTraverse(root, nodes);
return nodes;
}
private static void subPostOrderTraverse(BinaryNode root, List<int> nodes)
{
if(root != null)
{
subPostOrderTraverse(root.left, nodes);
subPostOrderTraverse(root.right, nodes);
nodes.Add(root.val);
}
}
postOrderTraverse
(五)广度优先搜索(breath first search, BFS),也叫作层次遍历,输出为:8,3,20,2,5,15,29,1,4,6,13,16,21,30。使用队列实现。

public static List<int>breathFirstSearch(BinaryNode root)
{
Queue<BinaryNode> queue = new Queue<BinaryNode>();
queue.Enqueue(root);
List<int> nodes = new List<int>();
while(queue.Count != 0)
{
BinaryNode node = queue.Dequeue();
nodes.Add(node.val);
if (node.left != null)
queue.Enqueue(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
queue.Enqueue(node.right);
}
return nodes;
}
breathFirstSearch
根据BSF的特点,可以实现二叉树的锯齿形层次遍历。leetcode103:给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值的锯齿形层序遍历,即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历。我用的方法如下:

public static List<List<int>>zigzagLevelOrder(BinaryNode root)
{
List<List<int>> nodes = new List<List<int>>();
Queue<BinaryNode> queue = new Queue<BinaryNode>();
queue.Enqueue(root);
int length = queue.Count;
while (queue.Count != 0)
{
List<int> _nodes = new List<int>();
while (length > 0)
{
BinaryNode node = queue.Dequeue();
_nodes.Add(node.val);
if (node.left != null)
queue.Enqueue(node.left);
if (node.right != null)
queue.Enqueue(node.right);
length--;
}
if (nodes.Count == 0)
nodes.Add(_nodes);
else if(nodes.Count ==1)
{
_nodes.Reverse();
nodes.Add(_nodes);
}
else
{
if (nodes.Count % 2 == 0)
nodes.Add(_nodes);
else
{
_nodes.Reverse();
nodes.Add(_nodes);
}
}
length = queue.Count;
}
return nodes;
}
zigzagLevelOrder
(六)二叉树的子树高度问题
leetcode平衡二叉树问题:给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。高度平衡意味着一个二叉树每个节点的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1.此问题可以转化为二叉树的子树高度问题。

public static bool isBalanced(BinaryNode node)
{
if (node == null)
return true;
if (Math.Abs(subTreeHeight(node.left) - subTreeHeight(node.right)) > 1)
return false;
return isBalanced(node.left) && isBalanced(node.right);
}
private static int subTreeHeight(BinaryNode node)
{
if (node == null)
return 0;
else
{
return Math.Max(subTreeHeight(node.left), subTreeHeight(node.right)) + 1;
}
}
binaryTreeHeight
类似地,还有求二叉树的最小深度问题,最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。例如root=[3,9,20,null,null,15,7],最小深度为2,即3-9两个节点。

public static int MinDepth(BinaryNode node)
{
if (node == null)
return 0;
if (node.left == null && node.right != null)
return MinDepth(node.right) + 1;
if (node.right == null && node.left != null)
return MinDepth(node.left) + 1;
return Math.Min(MinDepth(node.left) , MinDepth(node.right)) + 1;
}
minDpeth
